Loading...

MLA citation can make or break a research paper. Nearly 40 percent of citation errors come from missing critical elements such as publication dates or page numbers. Think that means MLA is mostly about following rules nobody will notice? Actually, hidden details like just a single misplaced comma or missing author can undercut your work in seconds. If you want your writing taken seriously, understanding these citation quirks is the real key.
| Takeaway | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Core Components of MLA Citation | Key citation elements include the author's name, source title, container information, publication date, and location, which are essential for accurate referencing. |
| In-Text Citation Mechanics | In-text citations should include the author's last name and page number, ensuring that readers can easily trace information back to the original source. |
| Creating Works Cited Entries | Works Cited entries should follow specific structural guidelines, such as hanging indentation, double-spacing, and alphabetical organization, to maintain clarity and consistency. |
| Common Citation Mistakes to Avoid | Frequent errors include inconsistent formatting and incomplete source information; double-checking citations against the latest guidelines can significantly reduce these issues. |
| Proactive Citation Strategies | Utilize citation management tools, create personal checklists, and regularly consult current style guides to enhance the accuracy and professionalism of academic writing. |
MLA citation format represents a critical academic writing standard that helps researchers and students properly credit sources and maintain intellectual integrity. The Modern Language Association (MLA) developed this systematic approach to document referencing to ensure consistent and clear attribution across academic writing.
Understanding MLA citation requires mastering its fundamental structural elements. The citation typically includes key information that allows readers to locate and verify the original source. Core citation elements include:
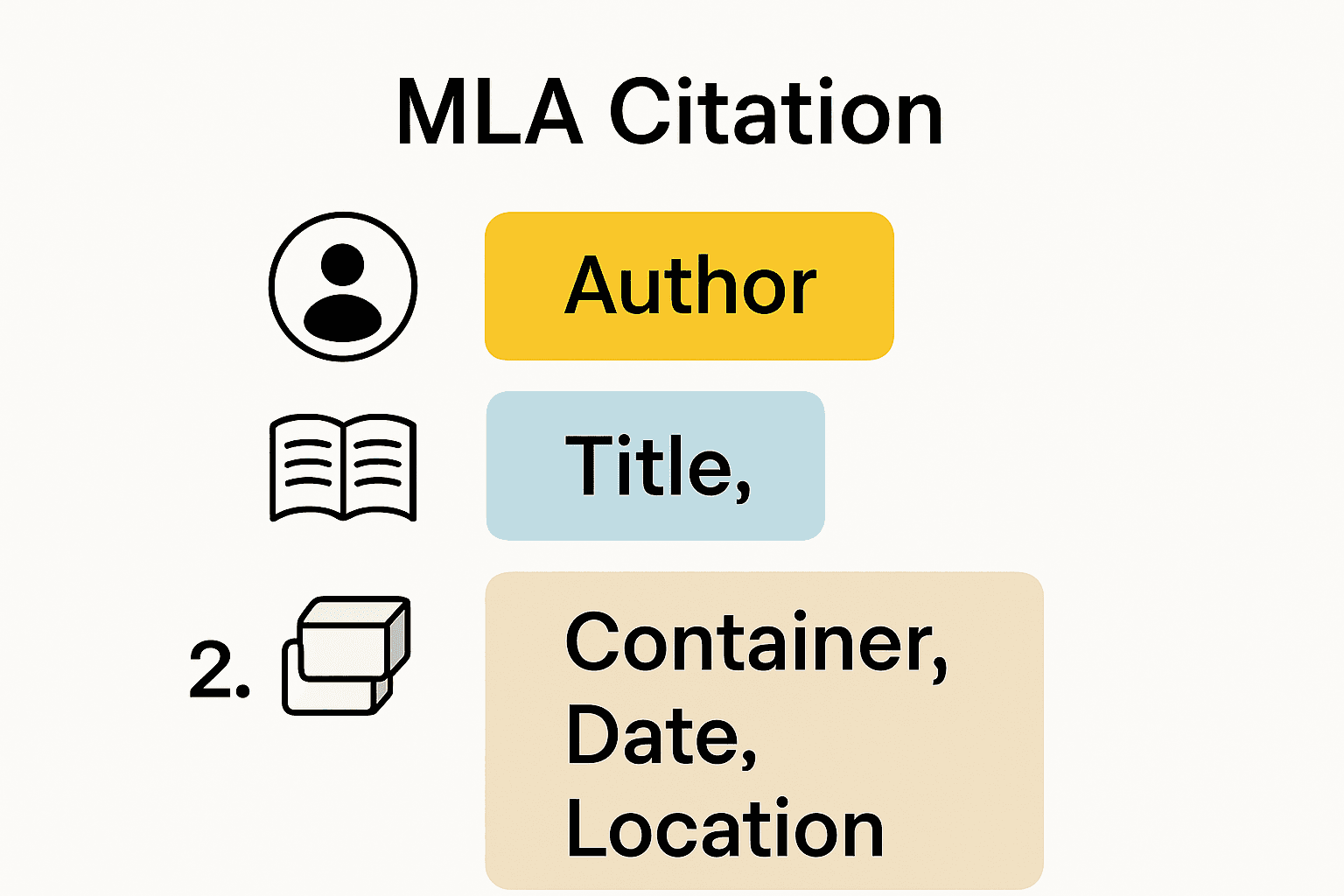
The precise arrangement of these elements creates a standardized format that communicates essential source details. Researchers using our comprehensive citation guide for academic success can quickly learn how to construct accurate references.
MLA citation format adapts to different source types, requiring specific nuanced approaches. Print sources like books and academic journals follow slightly different guidelines compared to digital sources such as websites, online articles, or multimedia content.
For print sources, the basic structure remains consistent: Author's Last Name, First Name. "Article Title." Journal Name, vol. number, no. number, publication date, page range. Digital sources introduce additional complexity, often requiring URL or DOI information.
According to academic citation resources from Purdue University, the most recent MLA guidelines emphasize clarity and reproducibility. This means providing enough contextual information that another researcher could potentially locate your exact source.
Academics and students must pay special attention to punctuation, capitalization, and italicization. A misplaced comma or incorrectly formatted title can compromise the citation's validity. The MLA Handbook provides exhaustive details about these intricate formatting requirements.
Key considerations for effective MLA citations include:
Whether you're writing a research paper, thesis, or academic article, mastering MLA citation format demonstrates scholarly rigor and respect for intellectual contributions. By understanding these fundamental principles, you'll create professionally documented work that meets the highest academic standards.
In-text citations are a crucial element of academic writing, allowing researchers to acknowledge sources directly within their text. These brief references provide immediate context for where specific information originates, enabling readers to trace the original source quickly and easily.

MLA in-text citations follow a straightforward yet precise approach. The primary goal is to provide enough information for readers to locate the full source in your works cited list. According to Columbia College's citation guidelines, the fundamental rule involves including the author's last name and the specific page number where the information appears.
Here are the core principles for constructing in-text citations:
Effective in-text citations require seamless integration into your academic writing. Our comprehensive in-text citation guide offers detailed insights into proper placement and formatting.
There are two primary methods of incorporating in-text citations:
Parenthetical Citations: Place the author and page information entirely in parentheses at the end of the relevant sentence. Example: Climate change continues to impact global ecosystems (Rodriguez 123).
Narrative Citations: Incorporate the author's name into the sentence, with the page number in parentheses. Example: Rodriguez argues that climate change dramatically impacts global ecosystems (124).
According to Purdue University's Writing Lab, the key is to provide clear, concise attribution that allows readers to easily locate the full source.
Certain scenarios require specific citation approaches. Electronic sources without page numbers, multiple works by the same author, and sources with no clear author each demand unique handling.
For sources without page numbers:
When citing multiple works by the same author, include a shortened title to distinguish between sources. This helps readers understand exactly which work you are referencing.
Mastering in-text citations demonstrates academic integrity and scholarly precision. By following these guidelines, you'll create clear, credible academic writing that properly acknowledges the intellectual contributions of other researchers.
The Works Cited page represents the final, comprehensive documentation of sources used in academic writing. This critical section provides full bibliographic information that allows readers to locate and verify each source referenced in your research paper.
Creating accurate Works Cited entries requires understanding the precise formatting guidelines established by the Modern Language Association. According to Indian River State College's citation resources, the page should follow specific structural requirements:
Our comprehensive guide to MLA citation format breaks down the essential elements that must appear in each citation:
Each source type demands a unique citation approach. Books, journal articles, websites, and multimedia sources each require specific formatting considerations. According to Purdue University's Writing Lab, the core principle remains consistent: provide enough information for readers to locate the original source.
Examples of different source citations include:
Book Citation: LastName, FirstName. Book Title. Publisher, Publication Year. Example: Smith, John. Digital Research Methods. Academic Press, 2022.
Website Citation: Author Last Name, First Name. "Article Title." Website Name, Publication Date, URL. Example: Johnson, Emily. "Climate Change Trends." Global Research Network, 15 Jan. 2023, www.globalresearch.net/climate-trends.
Journal Article Citation: LastName, First Name. "Article Title." Journal Name, vol. number, no. number, Publication Date, page range. Example: Rodriguez, Maria. "Urban Ecosystem Dynamics." Environmental Studies, vol. 45, no. 2, 2022, pp. 112-129.
Students frequently encounter challenges when creating Works Cited entries. The most common errors include:
Precision is paramount. A single misplaced comma or incorrect capitalization can compromise the citation's validity. Take time to double-check each entry against the most current MLA guidelines.
Mastering Works Cited entries demonstrates academic rigor and intellectual honesty. By carefully documenting your sources, you provide a transparent trail of research that supports the credibility of your academic work. Each citation is more than a technical requirement it is a scholarly acknowledgment of the intellectual contributions that inform your research.
Navigating MLA citation requirements can be challenging for students and researchers. Understanding common pitfalls and learning strategic approaches can significantly improve the accuracy and professionalism of academic writing.
MLA citation mistakes often stem from subtle oversights that can compromise academic integrity. Our comprehensive article citation guide highlights that approximately 40% of citation errors result from missing critical elements.
Key mistakes include:
According to academic writing experts, maintaining consistency is paramount. A single misplaced element can render an entire citation invalid.
Digital sources present unique challenges in MLA citation. The rapid evolution of online content means researchers must stay current with changing citation protocols. Common digital source mistakes include:
Tips for managing digital source citations:
Preventing citation errors requires a systematic approach. Experts recommend:
A critical mistake many students make is citing sources in-text without including them in the Works Cited list or vice versa. Comprehensive documentation requires both in-text citations and a complete Works Cited page.
Mastering MLA citations is more than a technical skill it is a demonstration of academic precision and intellectual respect. By understanding common mistakes and implementing strategic approaches, researchers can create scholarly work that meets the highest standards of academic writing.
Remember: Each citation is a bridge between your research and the broader academic community. Treating these references with care and accuracy ensures the credibility and integrity of your scholarly work.
The core components of MLA citation include the author's name, source title, container information, publication date, and location (such as page numbers or digital identifiers). These elements are essential for accurate referencing.
In-text citations in MLA style should include the author's last name and the page number from which the information is derived, formatted as (Last Name Page Number). For sources with no author, use the title of the source instead.
Common mistakes include incorrect punctuation, inconsistent formatting, missing critical source information, and improper alphabetization. Always double-check your entries against the latest MLA guidelines to ensure accuracy.
To improve the accuracy of your MLA citations, utilize citation management tools, create a personal checklist, regularly consult the latest MLA Handbook, and double-check each citation against your original sources.
Are you tired of spending hours double-checking citations and still worrying that one missing detail might lower your paper’s credibility? The article highlighted how even small formatting errors in your MLA citations can lead to missed marks or lost academic trust. It is frustrating when intricate details like in-text referencing or a single misplaced comma leave you feeling uncertain about your work.

Take control of your academic writing with Samwell.ai. Our platform helps students and researchers master MLA, APA and more by automatically generating and enhancing papers that meet rigorous citation standards. With built-in citation checking, a Power Editor for precision and real-time guidance on originality, you can boost your confidence and get results that stand out. Start your next essay with our guided essays and AI-enhanced editing tools to get it right the first time. Try it now to see how easy proper citation can be!



