Loading...

Academic citations might seem intimidating, especially when working with journal articles. Here is something you probably did not expect. Incorrect placement of a single parenthesis or a missing author name can cost you credibility and even lower your grade. Most guides focus on page numbers and author names as if that solves everything. The real difference maker is in mastering special cases like digital sources with no page numbers or handling three-author teams with 'et al.' If you want your sources to shine in 2025, attention to these overlooked details will give your citations the precision professors love.
| Takeaway | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Fundamental Structure of MLA Citations | In-text citations in MLA format include the author's last name and page number, e.g., (Smith 163), ensuring proper credit and traceability of sources. |
| Handling Multiple Authors | For citations with two authors, use both names, e.g., (Johnson and Lee 45). For three or more authors, use the first author's name followed by 'et al.', e.g., (Rodriguez et al. 22). |
| Citing Digital Sources | For digital articles without page numbers, cite only the author's last name in parentheses. If relevant, include paragraph numbers, aiding readers in locating content. |
| Common Mistakes to Avoid | Key errors include incorrect punctuation placement and incomplete citation information, such as omitting page numbers or author names, which can severely impact citation credibility. |
| Expert Tips for Accuracy | Always proofread citations against original sources to ensure correctness and check for dual authorship by utilizing shortened titles for works by the same author when necessary. |
MLA in-text citations represent a critical component of academic writing, providing a standardized method for acknowledging sources within research papers and scholarly documents. These citations help readers trace the origin of specific information and demonstrate the academic integrity of your research.
In MLA format, in-text citations follow a straightforward author-page number system. When referencing a journal article, you'll typically include the author's last name and the specific page number where the information appears. For example, a citation might look like (Smith 163), which indicates the information comes from page 163 of a work by an author named Smith.
The placement of these citations is crucial. Generally, you'll insert the parenthetical citation at the end of the sentence, before the period. If the author's name is already mentioned in the text, you only need to include the page number in parentheses. Check out our guide on citation specifics to master these nuanced rules.
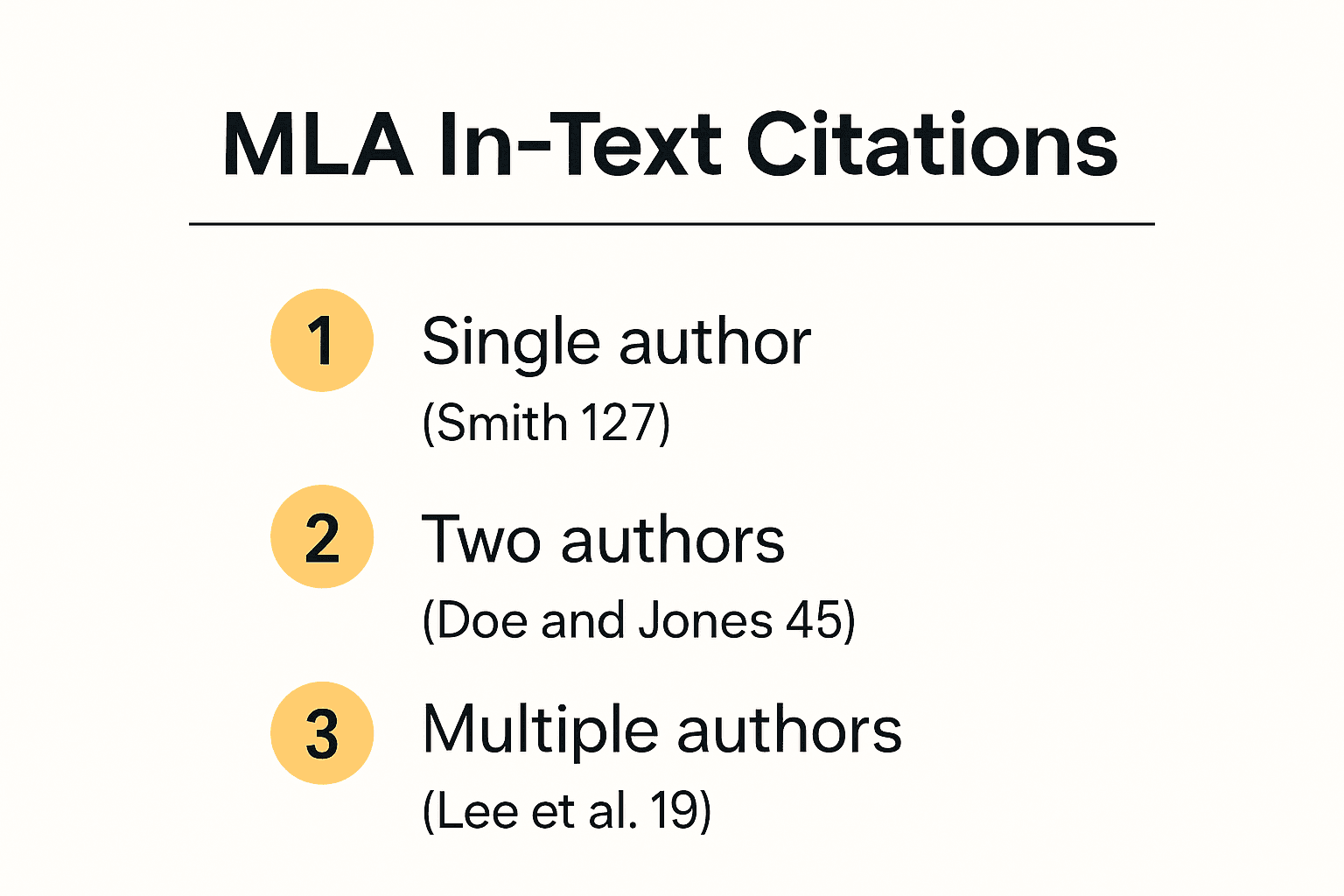
Multiple authors require slight modifications to the standard citation format. For two authors, you'll use both last names connected by "and" (Johnson and Lee 45). When three or more authors are involved, use the first author's last name followed by "et al." (Rodriguez et al. 22).
Some journal articles might present unique challenges. What happens when no page numbers are available? According to academic citation guidelines, you can simply use the author's last name in parentheses without a page number.
Digital journal articles accessed online might require additional considerations. While the core citation principles remain consistent, always prioritize providing enough information to help readers locate your original source. This means including clear identifying information like the author's name and, when possible, specific page or paragraph numbers.
Researchers should remember that accurate in-text citations serve multiple purposes. They not only give credit to original authors but also demonstrate the scholarly foundation of your work. By precisely following MLA guidelines, you show respect for intellectual property and contribute to the academic conversation with transparency and integrity.
Practicing these citation techniques becomes easier with consistent application. Start by carefully noting source details as you research, and develop a systematic approach to recording citation information. Over time, creating accurate MLA in-text citations will become second nature.
Formatting MLA in-text citations for journal articles requires precision and attention to detail. Mastering this skill ensures your academic writing meets professional standards and gives proper credit to original sources.
Before creating an in-text citation, gather essential information from the journal article. You'll need the author's last name and the specific page number where the referenced information appears. Learn the precise citation techniques to streamline your citation process.
The basic MLA in-text citation structure follows two primary scenarios:
Some journal articles present unique challenges that require special citation approaches. According to academic citation guidelines, here are specific strategies for different situations:
Multiple Authors
No Page Numbers
No Identified Author
Correct placement of in-text citations is crucial for maintaining academic writing standards. Always position the parenthetical citation at the end of the sentence, immediately before the period. If the author's name appears naturally in your text, include only the page number in parentheses.
Punctuation rules are straightforward:
Practicing these techniques consistently will help you develop muscle memory for creating accurate MLA in-text citations. Remember that clear, precise citations not only demonstrate academic integrity but also help readers trace and verify your research sources.
As you become more comfortable with MLA citation formatting, you'll find the process becomes more intuitive. Take time to review examples, practice with various source types, and always double-check your citations against the most current MLA guidelines.
Navigating MLA in-text citations becomes more complex when dealing with multiple authors, collaborative works, and unique source scenarios. Understanding these nuanced citation techniques ensures your academic writing remains precise and professional.
MLA citation guidelines provide clear frameworks for handling different author configurations. Learn advanced citation techniques to manage these intricate situations effectively.
For journal articles with multiple authors, the citation approach varies based on the number of contributors:
Two Authors
Three or More Authors
Some research scenarios require special citation considerations beyond standard multi-author formatting. Researchers must adapt their citation approach based on specific source characteristics.
Sources Without Page Numbers
Multiple Works by Same Author
Corporate or Institutional Authors
Researchers must remain adaptable and attentive to the specific requirements of each source. While these guidelines provide a comprehensive framework, always consult the most recent MLA style guide for the most up-to-date citation practices.
Practicing these citation techniques will help you develop confidence in handling complex referencing scenarios. Remember that clear, accurate citations not only demonstrate academic rigor but also provide readers with a transparent path to verifying your research sources.
As citation styles continue to evolve, staying informed about the latest MLA guidelines becomes increasingly important. Regularly reviewing and updating your citation knowledge ensures your academic writing remains current and professional.
Mastering MLA in-text citations requires careful attention to detail and an understanding of common pitfalls that can compromise the accuracy of your academic writing. Recognizing and avoiding these errors will significantly improve the quality of your research documentation.
Discover advanced citation strategies that can help you navigate the most challenging citation scenarios. Academic researchers often encounter several critical mistakes that can undermine their citation credibility:
Punctuation and Placement Mistakes
Incomplete Citation Information
According to academic citation guidelines, precision is key in creating reliable citations.
Professional researchers and academic writers recommend several strategies to ensure citation accuracy:
Proofread and Verify
Handling Complex Scenarios
Digital Source Considerations
Common mistakes can significantly impact the credibility of your research. Inexperienced researchers often overlook subtle nuances that can compromise citation accuracy. The most frequent errors include:
To avoid these pitfalls, develop a systematic approach to citation. Create a checklist that includes:
Remember that citation is more than a technical requirement. It's a way of acknowledging intellectual contributions and providing readers with a clear path to verify your research sources. Each citation tells a story of scholarly dialogue and intellectual exchange.
As academic writing continues to evolve, staying informed about the latest MLA guidelines becomes crucial. Regularly updating your citation knowledge ensures your academic work remains professional, credible, and transparent.
In MLA format, in-text citations for journal articles typically follow the author-page number system. For example, you would cite a source as (Smith 163) when referencing page 163 of a work by an author named Smith.
For articles with two authors, include both names in the citation, e.g., (Johnson and Lee 45). For three or more authors, use the first author's last name followed by 'et al.', e.g., (Rodriguez et al. 22).
For digital sources without page numbers, simply use the author's last name in parentheses, like this: (Smith). If necessary, include paragraph numbers to help readers locate the cited content.
Common mistakes include misplacing punctuation, omitting page numbers or author names, and inconsistent citation formatting throughout your document. Always double-check your citations to ensure they meet MLA guidelines.
Keeping up with MLA in-text citation details can leave you feeling frustrated and worried about losing points for small errors like forgotten page numbers or mixing up 'et al.' Crystal-clear citations matter for your grades and for your credibility but getting every rule right can be a headache. Why risk dropping your grade over misplaced parentheses or confusing multi-author situations when technology can simplify your workflow?

Experience academic relief by exploring Samwell.ai today. Our AI-driven tools automate perfect, MLA-compliant citations so you can focus on your research instead of formatting. Enjoy features like instant source attribution, built-in plagiarism safeguards, and a guided essay structure—all designed to help you meet the newest standards with confidence. Ready for clean and accurate citations in every paper? Visit Samwell.ai now and see why over one million students trust us for smarter, stress-free writing.



